Which Is An Example Of A Situation Where Differential Vulnerability Might Be A Factor: Real-World Scenarios

Differential vulnerability affects many situations in daily life. It highlights how different groups face risks differently.
Understanding this concept is crucial. Differential vulnerability refers to the varying levels of risk different groups face due to factors like age, gender, or socioeconomic status. For instance, during a natural disaster, children and elderly individuals are often more vulnerable compared to healthy adults.
This difference can be due to physical limitations, lack of resources, or even social support. Recognizing these vulnerabilities helps in creating better support systems and policies. It ensures that aid reaches those who need it the most, effectively reducing harm and promoting equality. In this blog, we will explore specific examples to illustrate differential vulnerability and its impact on various communities.
Defining Differential Vulnerability
Differential vulnerability refers to the varying levels of risk people face in different situations. It highlights how certain groups are more susceptible to harm due to various factors. Understanding this concept is crucial for recognizing and addressing inequalities.
Concept Overview
Differential vulnerability occurs when certain individuals or groups are more exposed to risks. These risks can be due to social, economic, or environmental factors. For example, during a natural disaster, some communities may suffer more due to their location or resources.
This concept helps in identifying which groups need more support and protection. By understanding who is most vulnerable, better policies and interventions can be designed.
Key Characteristics
- Social Factors: Include age, gender, and social status.
- Economic Factors: Involve income level and access to resources.
- Environmental Factors: Relate to living conditions and exposure to hazards.
Social factors play a significant role. Older adults and children often face higher risks. Economic factors are also critical. Low-income groups usually have fewer resources to cope with adverse events. Environmental factors affect those living in hazardous areas more.
| Factor | Examples |
|---|---|
| Social | Age, Gender, Disability |
| Economic | Income, Employment |
| Environmental | Housing, Pollution |

Credit: www.cell.com
Health Disparities
Health disparities refer to differences in health outcomes among different groups. These differences often stem from factors like socioeconomic status, race, and access to healthcare. Differential vulnerability plays a significant role in creating these disparities.
Access To Healthcare
Access to healthcare is crucial for maintaining good health. Unfortunately, not everyone has equal access. People in rural areas might lack nearby medical facilities. Similarly, low-income families often cannot afford healthcare. This limited access leads to poorer health outcomes.
A table below shows how access to healthcare varies among different groups:
| Group | Access Level |
|---|---|
| Urban Residents | High |
| Rural Residents | Low |
| High-Income Families | Very High |
| Low-Income Families | Very Low |
Chronic Illness Impact
Chronic illnesses like diabetes and hypertension affect different groups differently. For instance, minorities and low-income individuals are more likely to suffer from these conditions. They often have limited access to preventive care, leading to severe health issues.
Here are some factors contributing to the higher impact of chronic illnesses:
- Poor diet due to economic constraints
- Lack of exercise facilities in certain areas
- Limited health education
Addressing these factors can help reduce health disparities and improve overall health outcomes.
Economic Inequality
Economic inequality plays a significant role in differential vulnerability. It affects people’s ability to access basic needs and services. When economic inequality exists, some groups face more challenges than others. This creates disparities in well-being and opportunities.
Income Disparities
Income disparities are a major factor in economic inequality. People with higher incomes have more resources. They can afford better healthcare and education. Those with lower incomes struggle to meet basic needs. This increases their vulnerability in society. Wealthier individuals can recover from financial setbacks more easily. The gap between the rich and the poor continues to widen.
Employment Insecurity
Employment insecurity contributes to economic inequality. Many people work in unstable jobs. They do not have job security or benefits. This makes them more vulnerable to financial crises. People with secure jobs have consistent income and benefits. They are less affected by economic downturns. Employment insecurity impacts mental and physical health.
Those with unstable employment may face stress and anxiety. This can lead to health problems and further economic challenges. Addressing employment insecurity is crucial in reducing economic inequality.
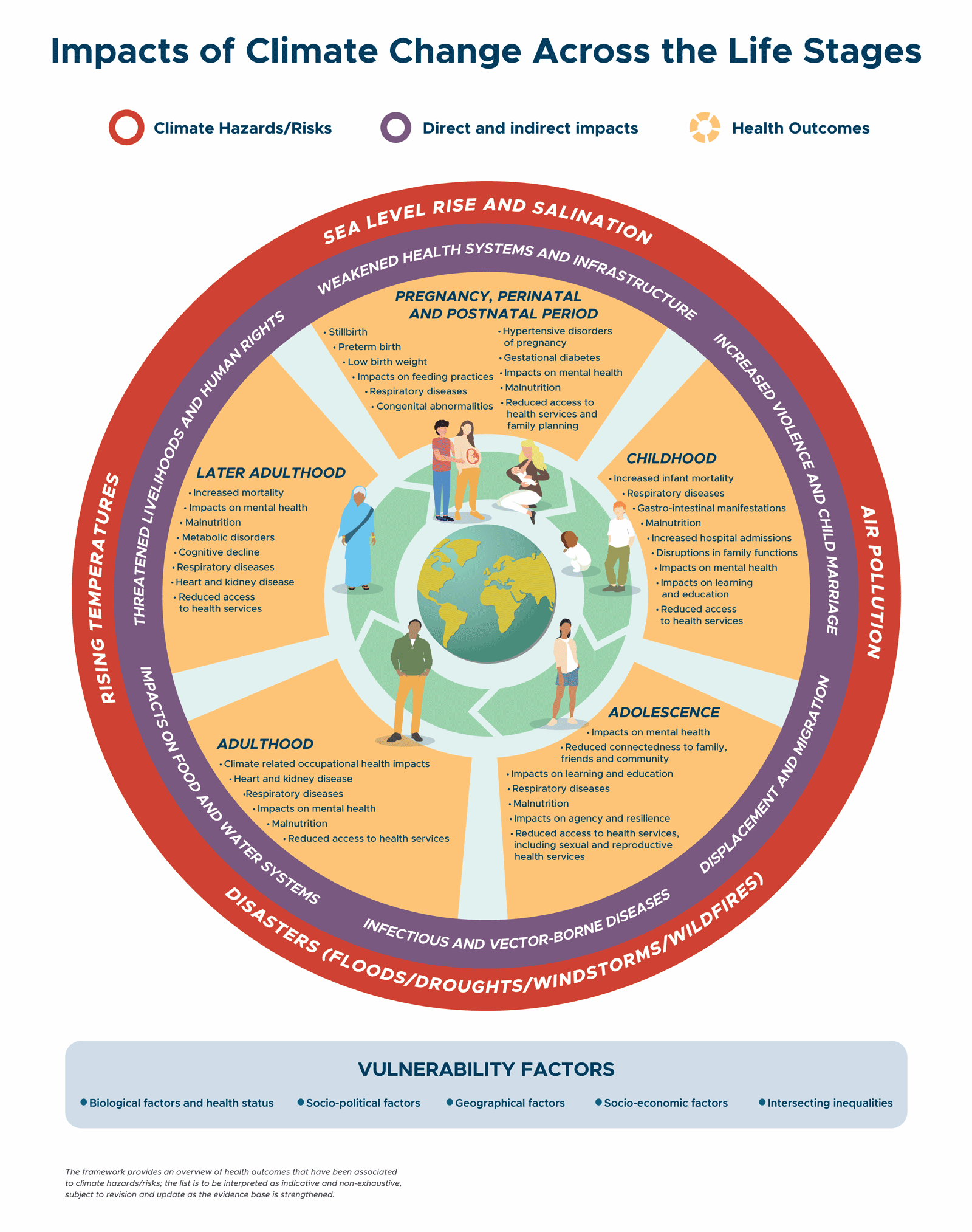
Credit: jogh.org
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a crucial role in differential vulnerability. These factors can affect people differently based on their location, health, and socioeconomic status. Two significant environmental factors are climate change and pollution. These can lead to severe health and economic impacts. Let’s explore how these factors contribute to differential vulnerability.
Climate Change Effects
Climate change is causing extreme weather events. These events include hurricanes, floods, and heatwaves. People living in low-income areas often suffer the most. They may lack resources to recover quickly. Homes in these areas are more likely to be damaged. Health services may be limited or hard to access.
Communities in coastal regions face rising sea levels. This can lead to displacement and loss of homes. People with limited mobility or chronic illnesses are at higher risk. They may find it hard to evacuate during emergencies. Climate change also affects food security. Droughts and floods can destroy crops. Poor communities might struggle to afford food.
Pollution Exposure
Pollution exposure varies based on where people live. Urban areas often have higher pollution levels. Industrial activities contribute to air and water pollution. Those living near factories or highways are more exposed. This can lead to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
Children and the elderly are more vulnerable to pollution. Their bodies are less capable of handling pollutants. Low-income communities might have limited access to clean air and water. They may also lack adequate healthcare.
Polluted water sources can cause serious health issues. Drinking contaminated water can lead to diseases like cholera. Communities with poor infrastructure are at higher risk. They may not have proper waste disposal systems. This can lead to water contamination and health risks.
Social Determinants
Social determinants play a critical role in shaping health outcomes. These factors influence how different people experience vulnerability. Understanding social determinants can help address health disparities.
Education Access
Education access is a significant social determinant. People with limited education often face more health challenges. They may lack knowledge about healthy behaviors. This can lead to poor health decisions. Education also impacts job opportunities. Lower education levels usually mean lower-paying jobs. This can make it hard to afford health care. Thus, limited education access increases health risks.
Housing Stability
Housing stability is another vital factor. People with unstable housing face higher health risks. They may live in unsafe environments. This can expose them to toxins or violence. Unstable housing also leads to stress. High stress levels can worsen health conditions. Moreover, frequent moves disrupt medical care. This makes it hard to maintain good health. Stable housing is crucial for a healthy life.
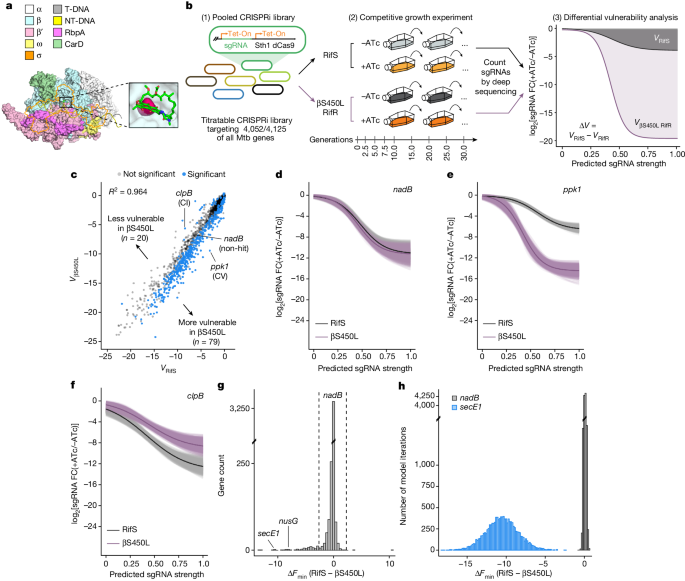
Credit: www.nature.com
Mental Health
Mental health is a crucial part of overall well-being. It affects how we think, feel, and act. Differential vulnerability refers to the varying levels of risk different individuals face under similar conditions. In the context of mental health, this concept can highlight why some people are more affected by mental health issues than others.
Stress And Anxiety
Stress and anxiety are common mental health challenges. They impact people differently based on their circumstances. For example, individuals with supportive networks might cope better. Those with fewer resources may struggle more.
Consider a workplace scenario. Two employees face the same deadline. One has a supportive family, the other does not. The latter might experience higher stress levels. This is an example of differential vulnerability.
Access To Mental Health Services
Access to mental health services is another area where differential vulnerability plays a role. Not everyone has the same access to care. Some communities have more resources. Others have limited or no access to mental health services.
For instance, rural areas often lack mental health professionals. Residents in these areas might suffer more. Urban areas usually have better access. This discrepancy can lead to significant differences in mental health outcomes.
Financial barriers also affect access. People with higher incomes can afford private therapy. Those with lower incomes might rely on public services, which are often overwhelmed.
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Social Support | Higher support reduces stress |
| Geographical Location | Urban areas have better services |
| Financial Resources | More resources mean better access |
Natural Disasters
During a hurricane, differential vulnerability becomes evident. Wealthier communities may have stronger buildings, while poorer areas suffer more damage. This disparity highlights how economic status impacts disaster resilience.
Natural disasters can strike at any moment. They leave behind a trail of destruction. Earthquakes, hurricanes, and floods can devastate entire communities. While all people face risks, some are more vulnerable than others. This is where differential vulnerability comes into play. Factors like age, income, and location can affect how people respond and recover.Vulnerability In Emergencies
During natural disasters, not everyone can escape harm. Some groups face higher risks. Older adults, children, and those with disabilities may need extra help. Low-income families often live in less sturdy homes. These homes can suffer more damage. People without cars may struggle to evacuate. These factors make them more vulnerable.Recovery Challenges
After a disaster, recovery can be tough. Some people bounce back faster than others. Those with savings and insurance can rebuild quicker. Low-income families may not have these resources. They might need to rely on government aid. This aid can be slow to arrive. Recovery can take years for them. Differential vulnerability means some people face harder challenges. “`Global Perspective
Understanding differential vulnerability from a global perspective is crucial. This concept explains why some groups face more risks during crises. These can range from natural disasters to economic downturns. Different factors, such as location, economic status, and social structures, influence vulnerability.
Developing Countries
In developing countries, differential vulnerability is often more pronounced. People in these regions face numerous challenges. Many lack access to basic services such as healthcare, education, and clean water. These deficiencies increase their risk during crises.
A table can help illustrate the differences:
| Factor | Developed Countries | Developing Countries |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare Access | High | Low |
| Education | Universal | Limited |
| Infrastructure | Advanced | Basic |
These disparities highlight the need for targeted interventions. Improving access to resources can reduce vulnerability.
Policy Interventions
Policy interventions play a significant role in addressing differential vulnerability. Governments and organizations must implement effective strategies. Below are some key policy interventions:
- Healthcare improvements: Ensure universal healthcare access
- Education programs: Increase educational opportunities
- Infrastructure development: Build resilient infrastructure
- Social protection: Provide safety nets for the vulnerable
These interventions can significantly reduce vulnerability. They help build resilient communities. Proper implementation is key to their success.
A strong focus on policy can mitigate risks and improve lives globally.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Differential Vulnerability?
Differential vulnerability refers to varying levels of susceptibility to harm among individuals or groups due to differences in social, economic, or biological factors.
How Does Differential Vulnerability Affect Health?
Differential vulnerability affects health by creating disparities in how different groups experience and cope with health-related risks and outcomes.
Can Differential Vulnerability Be Linked To Socioeconomic Status?
Yes, socioeconomic status often influences differential vulnerability, as lower socioeconomic groups may have less access to resources and support systems.
How Does Gender Influence Differential Vulnerability?
Gender can influence differential vulnerability by dictating roles, responsibilities, and access to resources, leading to different risk levels for men and women.
Conclusion
Differential vulnerability affects many situations in everyday life. It can impact health, safety, and economic stability. Understanding these factors helps in creating better support systems. Different groups face unique challenges. Recognizing these helps in reducing risks. For example, elderly people may need more health care resources.
Addressing these differences improves overall well-being. Everyone deserves equal opportunities and protection. Awareness and action can make a big difference. Let’s work together for a fairer world.



