How Are The Processes Of Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Interrelated: A Symbiotic Dance
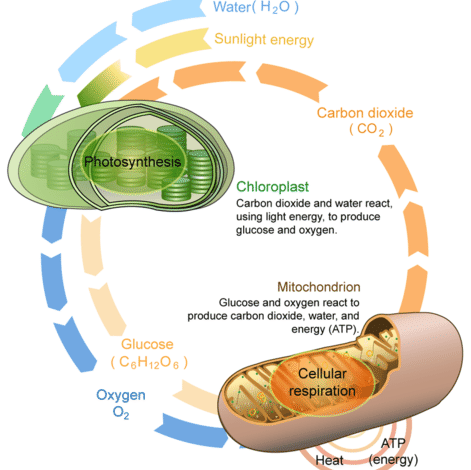
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two vital processes. They are crucial for energy conversion in living organisms.
But how are they interrelated? Photosynthesis and cellular respiration might seem like opposite processes. Yet, they are deeply connected. Photosynthesis occurs in plants, converting sunlight into energy. Cellular respiration happens in all living cells, releasing energy from food. These processes form a cycle of energy and matter, making life possible.
Understanding their relationship helps us grasp how energy flows through ecosystems. It also shows the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. In this blog, we will explore how these processes work together. We will see their roles in maintaining life on Earth. Stay with us to uncover the fascinating links between photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
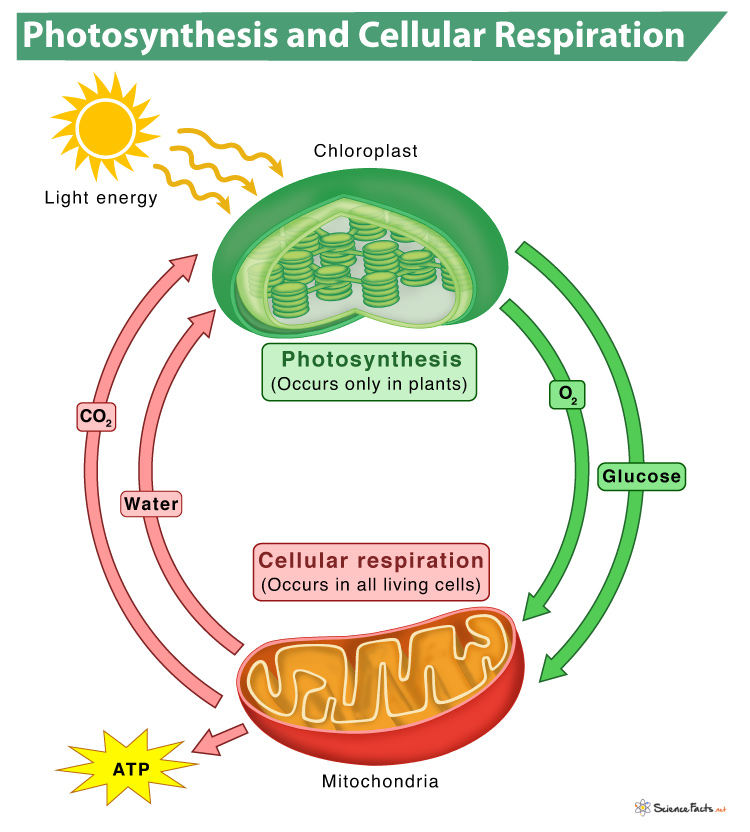
Credit: www.sciencefacts.net
Introduction To Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are interconnected. Photosynthesis produces glucose and oxygen, used by cellular respiration. Cellular respiration generates carbon dioxide and water, essential for photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are essential biological processes. They play a vital role in the energy cycle of living organisms. Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, and some bacteria. Cellular respiration happens in nearly all living organisms, including plants and animals.Basic Concepts
Photosynthesis converts sunlight into chemical energy. Plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen. The process takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells. The formula for photosynthesis is simple: 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy -> C6H12O6 + 6O2. Cellular respiration breaks down glucose for energy. Organisms use oxygen to convert glucose into ATP, water, and carbon dioxide. This process occurs in the mitochondria of cells. The formula for cellular respiration is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy (ATP).Importance To Life
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are interdependent processes. Photosynthesis provides oxygen and glucose. Cellular respiration uses these products to generate energy. The oxygen released during photosynthesis is vital for breathing. Plants and animals rely on this oxygen for survival. Glucose produced in photosynthesis serves as a fuel for cellular respiration. This continuous exchange forms a balanced cycle. It maintains the atmosphere’s oxygen and carbon dioxide levels. Both processes are crucial for life on Earth. They ensure the flow of energy through ecosystems. “`Photosynthesis Process
The photosynthesis process converts light energy into chemical energy. Plants use this energy to make food. This process takes place in chloroplasts. There are two main stages: Light Reactions and the Calvin Cycle.
Light Reactions
The Light Reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes. They capture sunlight and convert it to energy. This energy is stored in two molecules: ATP and NADPH.
- Light hits chlorophyll, exciting electrons.
- Electrons move through the electron transport chain.
- Water splits, releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
- ATP and NADPH are produced.
Calvin Cycle
The Calvin Cycle takes place in the stroma. It uses ATP and NADPH to convert carbon dioxide into glucose. This process does not require light, hence it is also called the dark reaction.
- Carbon dioxide enters the cycle.
- ATP and NADPH provide energy and electrons.
- Glucose is formed after a series of reactions.
In summary, the Calvin Cycle creates sugar, which plants use as food. This sugar is crucial for the next stage: Cellular Respiration.
Cellular Respiration Process
Cellular respiration is a vital process in living organisms. It converts glucose into ATP, the energy currency of cells. This process consists of three main stages: Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and Electron Transport Chain.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the first step of cellular respiration. It happens in the cytoplasm of the cell. During glycolysis, one molecule of glucose is split into two molecules of pyruvate. This process produces a small amount of ATP and NADH.
Here is a simple breakdown of glycolysis:
- Glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate.
- ATP is produced through substrate-level phosphorylation.
- NADH is generated as electrons are transferred.
Glycolysis does not require oxygen. It is an anaerobic process.
Krebs Cycle
The Krebs Cycle, also known as the Citric Acid Cycle, occurs in the mitochondria. This cycle processes each pyruvate molecule from glycolysis. It releases energy stored in acetyl-CoA through a series of reactions.
Key points of the Krebs Cycle include:
- Each pyruvate is converted into Acetyl-CoA.
- ATP, NADH, and FADH2 are produced.
- Carbon dioxide is released as a waste product.
The Krebs Cycle is aerobic, meaning it requires oxygen.
Electron Transport Chain
The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) is the final stage of cellular respiration. It occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The ETC uses electrons from NADH and FADH2 to create a proton gradient. This gradient powers ATP synthase to produce ATP.
Important steps in the Electron Transport Chain:
- Electrons are transferred from NADH and FADH2 to proteins in the ETC.
- Protons are pumped across the mitochondrial membrane, creating a gradient.
- ATP synthase uses this gradient to produce ATP.
- Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor, forming water.
The Electron Transport Chain is also aerobic. Oxygen is essential for the process.
In summary, cellular respiration is a multi-step process. It efficiently converts glucose into ATP, providing energy for cellular functions.
Energy Conversion
The processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration are essential for energy conversion in living organisms. These two processes are interconnected and play a crucial role in the energy cycle. Photosynthesis converts solar energy into chemical energy, while cellular respiration converts that chemical energy into a usable form for cells.
Atp Production
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the energy currency of cells. During photosynthesis, plants use sunlight to create glucose. In cellular respiration, cells break down glucose to produce ATP.
Here is a simple table to show the process:
| Process | Energy Source | Energy Product |
|---|---|---|
| Photosynthesis | Sunlight | Glucose |
| Cellular Respiration | Glucose | ATP |
ATP is used by cells to perform various functions like muscle contraction and cell division.
Role Of Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar that plays a key role in energy storage. During photosynthesis, plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This glucose serves as an energy reserve.
In cellular respiration, glucose is broken down in the presence of oxygen to produce ATP, water, and carbon dioxide. This process occurs in the mitochondria of cells.
Here is a simple ordered list of the steps involved in cellular respiration:
- Glycolysis: Breaks down glucose into pyruvate.
- Citric Acid Cycle: Produces energy carriers.
- Electron Transport Chain: Generates ATP.
Both processes are vital for the survival of plants and animals. They ensure a continuous flow of energy through the ecosystem.
Exchange Of Gases
The exchange of gases is a vital process in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration. These two processes are interconnected through the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Plants produce oxygen through photosynthesis, which is then used by animals and plants in cellular respiration. This creates a continuous cycle that supports life on Earth.
Oxygen Production
During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide and water. They use sunlight to convert these into glucose and oxygen. This process happens in the chloroplasts of plant cells. The oxygen produced is released into the atmosphere. Animals and other organisms then use this oxygen for cellular respiration.
Here is a simple representation of the process:
| Photosynthesis | Cellular Respiration |
|---|---|
| 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy | C6H12O6 + 6O2 |
| = C6H12O6 + 6O2 | = 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy |
Carbon Dioxide Utilization
In cellular respiration, living organisms break down glucose to produce energy. This process requires oxygen and releases carbon dioxide as a byproduct. This carbon dioxide is then utilized by plants during photosynthesis. The cycle repeats, ensuring a balance of gases in the atmosphere.
Important points to note:
- Photosynthesis produces oxygen.
- Cellular respiration uses oxygen.
- Cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide.
- Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide.
This interdependence highlights the importance of both processes in maintaining life on Earth. Understanding this cycle helps us appreciate the balance and harmony in nature.
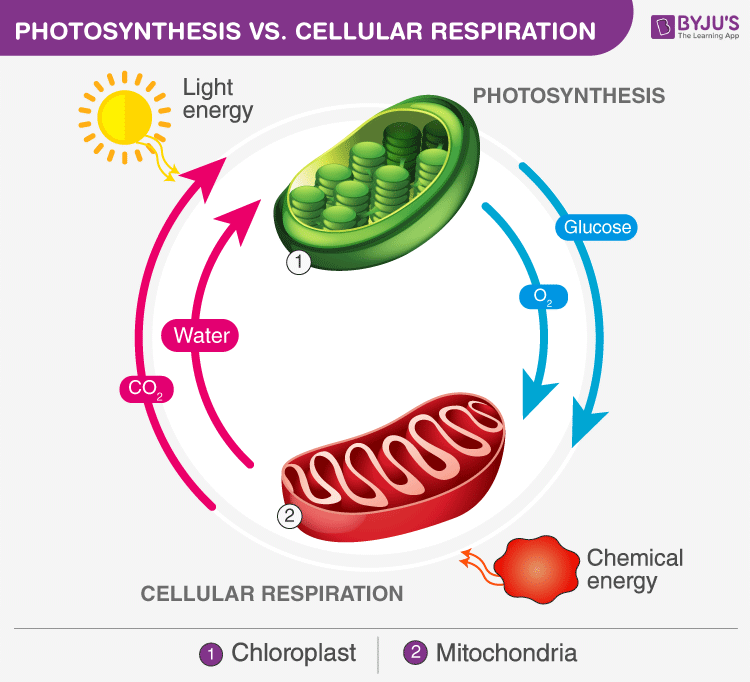
Credit: byjus.com
Interdependence Of Processes
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are interdependent. Plants produce oxygen and glucose through photosynthesis. Animals use these products in cellular respiration to generate energy and release carbon dioxide, which plants use to perform photosynthesis. This cycle sustains life on Earth.
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two crucial biological processes. They are essential for life on Earth. These processes depend on each other. They form a cycle that sustains life. Let’s explore how they are interrelated.Energy Flow
Photosynthesis converts sunlight into chemical energy. Plants use this energy to produce glucose. This glucose is stored in their cells. Animals eat plants and use this stored energy. Cellular respiration releases this energy for use by cells. This energy flow supports all living organisms.Nutrient Cycles
Photosynthesis produces oxygen as a byproduct. This oxygen is essential for cellular respiration. Animals and plants use it to break down glucose. Cellular respiration releases carbon dioxide. Plants need this carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. This cycle keeps the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. “`Environmental Impact
The processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration are essential for life on Earth. They play a key role in maintaining the balance of the environment. Understanding their environmental impact helps us appreciate their significance. These processes are interconnected and impact the carbon cycle and global oxygen levels.
Carbon Cycle
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are part of the carbon cycle. During photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air. They use it to create glucose and oxygen. This process removes carbon dioxide, helping reduce greenhouse gases.
Cellular respiration, on the other hand, releases carbon dioxide back into the air. Animals and plants break down glucose for energy. This releases carbon dioxide and water. The carbon cycle depends on both processes to keep carbon levels stable. It is a delicate balance that sustains life.
Global Oxygen Levels
Photosynthesis produces oxygen as a byproduct. Plants and algae release this oxygen into the atmosphere. It is essential for the survival of most living organisms.
Cellular respiration consumes oxygen to break down glucose. This process provides energy for cells. While it uses oxygen, it also produces carbon dioxide. The balance between photosynthesis and respiration affects global oxygen levels. Without enough photosynthesis, oxygen levels would drop. This could lead to serious consequences for life on Earth.
Applications And Implications
The processes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration are essential for life. They play a crucial role in various fields. Understanding their applications and implications can help us tackle many global challenges.
Agriculture
Photosynthesis helps plants grow by converting sunlight into energy. Better understanding of this process can improve crop yields. Farmers can use this knowledge to grow more food. This helps feed a growing population. Cellular respiration is also important. It provides energy for plant growth and development. Efficient cellular respiration means healthier plants. Healthier plants lead to better harvests.
Climate Change
Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This helps reduce greenhouse gases. Plants and trees act as carbon sinks. They store carbon dioxide and release oxygen. This process is vital in combating climate change. Cellular respiration releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. Balancing these processes is key. It helps maintain a stable climate. Studying these processes can inform climate policies.

Credit: byjus.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Are Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Related?
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are interconnected processes. Photosynthesis converts light energy into glucose. Cellular respiration uses glucose to produce energy. Together, they form a cycle of energy transformation in living organisms.
Do Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Form A Cycle?
Yes, they form a cycle. Photosynthesis produces oxygen and glucose. Cellular respiration uses these to produce energy, carbon dioxide, and water, which are then used in photosynthesis.
What Role Does Glucose Play In Both Processes?
Glucose is essential in both processes. It is produced during photosynthesis. Cellular respiration then breaks down glucose to release energy required for cellular activities.
Why Are Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Important?
They are crucial for life. Photosynthesis provides oxygen and organic compounds. Cellular respiration converts these into usable energy, supporting life functions.
Conclusion
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are crucial for life. They depend on each other. Photosynthesis makes glucose and oxygen. Plants and some bacteria use this process. Cellular respiration breaks down glucose. It releases energy for cells. Animals and plants rely on this energy.
Both processes keep life balanced. They cycle carbon dioxide and oxygen. This supports ecosystems and life on Earth. Understanding these processes helps us appreciate nature’s harmony.



