What Was The Most Significant Result Of The Ruling In Marbury V Madison: Judicial Review
The most significant result of the ruling in Marbury v. Madison was the establishment of judicial review. This landmark decision in 1803 allowed the Supreme Court to declare laws unconstitutional.
Marbury v. Madison is a cornerstone of American legal history. The case began with a dispute between William Marbury and James Madison. The case’s outcome reshaped the balance of power in the U. S. Government. The ruling granted the judiciary the power to check the other branches of government.
This decision ensured that no law could violate the Constitution. This important case still influences the legal system today. Understanding its impact helps us appreciate the role of the judiciary in protecting our rights and freedoms.
Credit: www.womenfutureconference.com
Introduction To Marbury V. Madison
Marbury v. Madison is a landmark case in American history. It established the principle of judicial review. This ruling gave the Supreme Court the power to declare laws unconstitutional. The case was decided in 1803 and has shaped the U.S. legal system ever since.
Historical Context
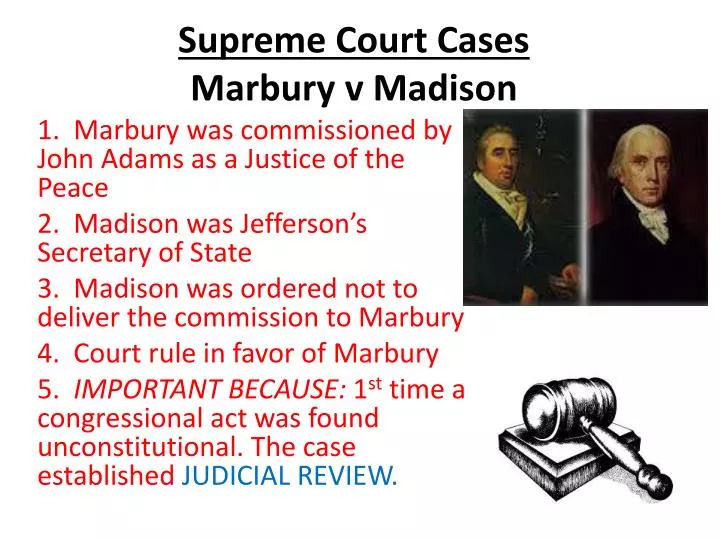
The case came about in the early 1800s. John Adams was the outgoing president. He made several last-minute judicial appointments. These appointments were part of the “Midnight Judges Act.”
Thomas Jefferson, the incoming president, opposed these appointments. He instructed his Secretary of State, James Madison, not to deliver the commissions. William Marbury, one of the appointees, sued for his commission. This led to the historic case known as Marbury v. Madison.
Key Players
Several key figures were involved in the case:
- William Marbury: The plaintiff who sued for his commission.
- James Madison: The Secretary of State who withheld the commission.
- John Adams: The outgoing president who made the appointments.
- Thomas Jefferson: The incoming president who opposed the appointments.
- John Marshall: The Chief Justice who delivered the ruling.
Each of these individuals played a crucial role. Their actions and decisions had a lasting impact on American law.
Background Of The Case
The case of Marbury v. Madison is a cornerstone of American law. It established the principle of judicial review. This case decided the role of the Supreme Court in the American government. Here’s a closer look at the background of this historic decision.
Events Leading Up
In 1801, President John Adams faced the end of his term. He appointed several judges in his last days. These judges were known as the “Midnight Judges.” The goal was to keep Federalist influence in the government. One of these judges was William Marbury.
Adams’ successor, Thomas Jefferson, took office. His Secretary of State, James Madison, refused to deliver Marbury’s commission. This prevented Marbury from taking his judicial position. Marbury then sued Madison, seeking a writ of mandamus. This legal order would compel Madison to deliver the commission.
Main Issues
The case raised several important questions:
- Did Marbury have a right to his commission?
- Could the court provide a remedy for Marbury?
- Did the Supreme Court have the authority to issue a writ of mandamus?
Chief Justice John Marshall delivered the opinion of the court. He ruled that Marbury had a right to his commission. The court also found that Marbury could seek a remedy. However, the Supreme Court did not have the power to issue a writ of mandamus. The Judiciary Act of 1789, which gave the court this power, was unconstitutional.
| Key Figures | Roles |
|---|---|
| John Adams | Outgoing President |
| Thomas Jefferson | Incoming President |
| James Madison | Secretary of State |
| William Marbury | Appointed Judge |
| John Marshall | Chief Justice |
The ruling in Marbury v. Madison established the principle of judicial review. This allowed the Supreme Court to declare laws unconstitutional. This case set a precedent that still affects the U.S. legal system today.
The Supreme Court Decision
The Marbury v. Madison case in 1803 was a landmark decision. It marked a turning point in American judicial history. The Supreme Court, under Chief Justice John Marshall, made a crucial ruling. This decision set the precedent for judicial review in the United States. It established the power of the courts to declare laws unconstitutional.
Court’s Rationale
The Court’s rationale was based on the Constitution. The justices believed the Constitution was the supreme law of the land. Any law conflicting with the Constitution was invalid. They used this principle to justify their decision. The case involved William Marbury, who had been denied his commission. The Court decided it had no power to enforce his commission. But it had the authority to interpret the law’s constitutionality.
Key Findings
The Supreme Court made several key findings in Marbury v. Madison. First, it established judicial review. This meant the Court could strike down laws violating the Constitution. Second, it clarified the role of the judicial branch. The Court stated it was its duty to say what the law is. Lastly, it emphasized the importance of the Constitution. The Constitution was the highest law, above any other laws.
Establishment Of Judicial Review
The ruling in Marbury v. Madison was a historic moment in U.S. history. It laid the foundation for the establishment of judicial review. This concept has shaped the American legal system significantly.
Definition
Judicial review is the power of courts to examine laws and actions. It ensures they comply with the Constitution. This authority was not explicitly stated in the Constitution. The Marbury v. Madison case clarified this power for the judiciary.
Importance
Judicial review is crucial for maintaining the balance of power. It allows courts to invalidate laws that violate the Constitution. This prevents any branch of government from becoming too powerful.
It also protects citizens’ rights. Courts can strike down unfair laws. This ensures justice and equality under the law. The establishment of judicial review has had lasting impacts. It continues to be a vital aspect of the American legal system.
Impact On The Judicial Branch
The ruling in Marbury v. Madison had a profound impact on the judicial branch. It established the principle of judicial review, giving the Supreme Court the power to declare laws unconstitutional. This decision elevated the role and authority of the judiciary within the U.S. government.
Increased Authority
Marbury v. Madison greatly increased the authority of the judicial branch. The Supreme Court gained the power to interpret the Constitution. This decision allowed the Court to invalidate laws that conflicted with the Constitution. As a result, the judiciary became a co-equal branch of government.
Checks And Balances
The ruling reinforced the system of checks and balances within the U.S. government. By allowing the judiciary to review and nullify congressional acts, it ensured that no single branch could dominate. This balance of power is crucial to maintaining democratic governance.

Credit: www.alhudapk.com
Long-term Effects On U.s. Law
The ruling in Marbury v. Madison had a profound impact on U.S. law. It established the principle of judicial review, changing the judiciary’s role. This decision allowed courts to strike down laws deemed unconstitutional.
The long-term effects of this ruling are vast and far-reaching. It shaped how laws are interpreted and enforced. The ruling also influenced many future legal decisions in the United States.
Precedents Set
Marbury v. Madison set important legal precedents. It established the judiciary’s authority to review and nullify laws. This power is crucial for maintaining checks and balances. It ensures no branch of government exceeds its authority.
This ruling also reinforced the Constitution as the supreme law. It emphasized the judiciary’s role in protecting constitutional rights. Many landmark cases have cited Marbury v. Madison as a precedent.
Influence On Future Cases
The ruling in Marbury v. Madison influenced many future cases. Courts continue to use judicial review to uphold constitutional principles. This decision paved the way for more robust judicial oversight.
Many significant cases have relied on Marbury v. Madison’s principles. It set the foundation for decisions that protect civil liberties. This ruling remains a cornerstone of U.S. legal practice.
Criticism And Controversy
The ruling in Marbury v. Madison sparked significant debate and controversy. Critics and supporters have expressed varied opinions about its implications. This section explores the criticisms and controversies surrounding the decision.
Opposing Views
Critics argue that the decision in Marbury v. Madison overstepped judicial boundaries. They believe it granted too much power to the judiciary. Opponents fear the ruling undermines the balance of power among the branches. This decision established the principle of judicial review. Some view this as an overreach of judicial authority. They worry it allows judges to make laws rather than interpret them.
Supporters, on the other hand, argue the decision was necessary. They contend it provided a crucial check on legislative and executive power. Proponents believe judicial review ensures laws remain constitutional. They argue this power is essential for protecting individual rights. The ruling, they say, strengthens the judiciary’s role in maintaining legal integrity.
Modern Perspectives
Modern scholars continue to debate the impact of Marbury v. Madison. Some view it as a foundational element of American democracy. They argue it set a precedent for judicial independence. Others believe the ruling’s effects have been overstated. They suggest it has led to an imbalance of power among the branches.
Recent discussions also focus on the role of the judiciary in contemporary politics. Some critics argue that judicial review has been used to advance political agendas. They believe this undermines the impartiality of the courts. Supporters counter that judicial review remains a vital tool. They argue it helps protect constitutional rights against legislative and executive overreach.

Credit: www.alhudapk.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Was The Marbury V. Madison Ruling?
The Marbury v. Madison ruling established the principle of judicial review. It allowed the Supreme Court to declare laws unconstitutional. This decision significantly increased the power of the judiciary.
Why Is Marbury V. Madison Important?
Marbury v. Madison is important because it established judicial review. This allows the Supreme Court to interpret the Constitution. It strengthened the role of the judiciary in government.
Who Was Involved In Marbury V. Madison?
The case involved William Marbury and James Madison. Marbury was appointed Justice of the Peace. Madison, as Secretary of State, withheld Marbury’s commission, leading to the lawsuit.
What Year Was Marbury V. Madison Decided?
Marbury v. Madison was decided in 1803. The case is one of the most important in U. S. legal history. It set a significant precedent for judicial authority.
Conclusion
The ruling in Marbury v. Madison reshaped American law significantly. It established judicial review. This means courts can strike down unconstitutional laws. This decision strengthened the judiciary’s role. It balanced power among government branches. Understanding this case helps grasp U.
S. Legal foundations. Its impact remains vital today. This ruling’s importance cannot be understated. It defined the court’s authority clearly. This case continues to influence legal decisions. Marbury v. Madison is a cornerstone of American democracy.



